I was recently tasked with setting up a MongoDB Replicaset.
Documentation for setting up a MongoDB Replicaset with OpsWorks was a bit on the sparse side and took a bit of trial and error. I ended up with this solution.
The Chef Recipe
The chef recipe used for this post is https://github.com/netinlet/chef-mongodb_replicaset
OpsWorks allows you to use custom recipes. All dependent recipes should be included in the custom cookbook.
The mongodb recipe depends on apt, python, runit and yum recipes.
Several recipes require the build-essentials recipes and the runit
recipe depends upon yum-epl.
The dependencies for this cookbook were pulled from the OpsCode public cookbooks. https://github.com/opscode-cookbooks
The mongodb recipe is custom. I ended up using this recipe
referenced in the presenation AWS OpsWorks under the hood.
The custom recipe is based off of https://github.com/edelight/chef-mongodb with OpsWorks specific code to properly setup replicasets in AWS OpsWorks.
OpsWorks Setup
I’m going to assume some degree of familiarity with OpsWorks. If you are new to AWS OpsWorks, you can get an overview here: http://aws.amazon.com/opsworks/
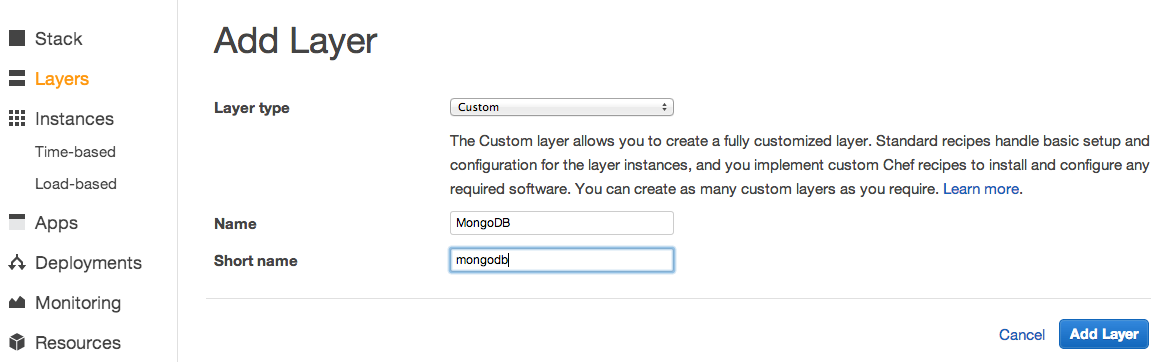
Add a MongoDB layer to your stack
Create a “Custom” layer named MongoDB and add it to the stack.
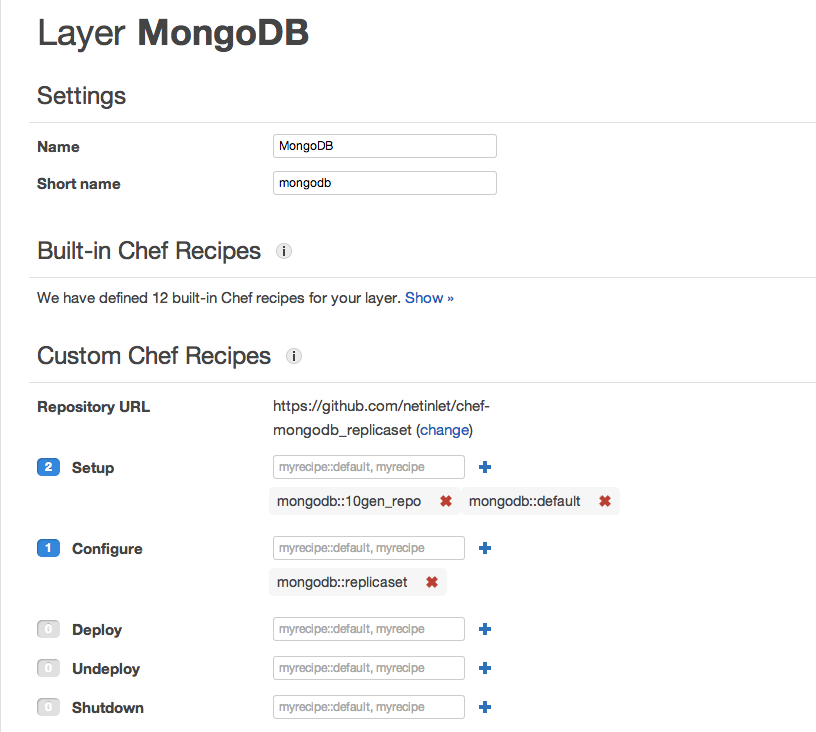
Configure the MongoDB layer
A custom layer is pre-defined with 12 built-in recipes. Nothing to do or change here.
Custom Chef Recipe Section
Repository URL Set the repository URL to the location of your chef recipe. This repository can be a link to a Git or Subversion repository or an http or S3 url. The custom recipe is configured in the Stack settings in which your layer lives. In this case, I have it pointed to my Github chef recipe.
OpsWorks has 5 lifecycle events which can be used to execute Chef recipe
steps. These events are setup, configure, deploy,
undeploy and shutdown. For this recipe, we will use the
setup and configure events.
Setup event Add mongodb::10gen_repo and
mongodb::default. The former configures the service to use the
10Gen MongoDB builds. The latter installs MongoDB and does a basic
single node configuration.
Configure event Add mongodb::replicaset. This event
configures the MongoDB instance as a member of a replicaset.
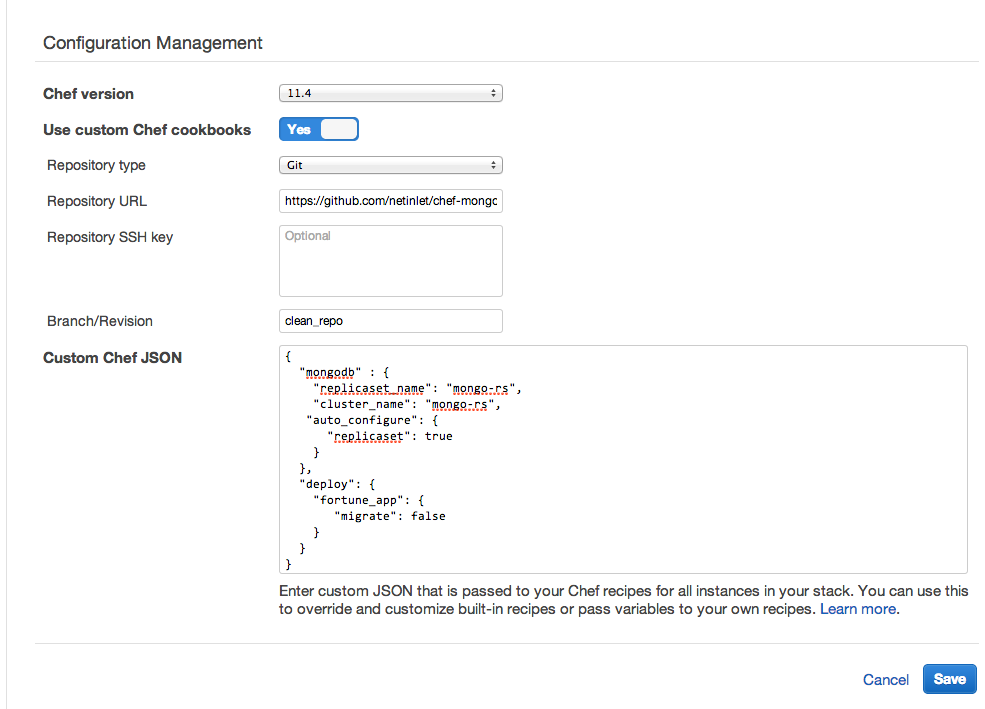
Custom Chef JSON In order for the replicaset to be configured properly, we have to specify the name of the replicaset, cluster and tell the instance to auto-configure.
The replicaset_name and cluster_name must match. You must also
set the auto_configure:replicaset hash value to true so the
replicaset is auto-configured on boot.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
Screenshot of editing the Stack where the custom recipe and Chef JSON are configured
Boot your MongoDB Instances
Add some instances to the MongoDB layer and boot them. An odd number of instances (3 or more) is the proper way to configure a replicaset without an arbiter.
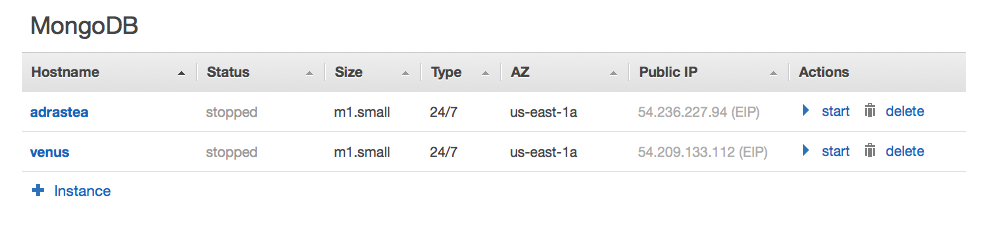
Unfortunately, on first boot the primary replicaset member is unable to communicate with the secondary replicaset member. I was unable to determine exactly why this happens but suspect a timing issue with the availability of the secondary replicaset member.
This is evident in the logs of the second instance. This error indicates the node was unreachable at the time it was being configured. See line 4.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
The work-around is to run the mongodb::replicaset recipe again
from the Stack section of OpsWorks with the Run Command button.
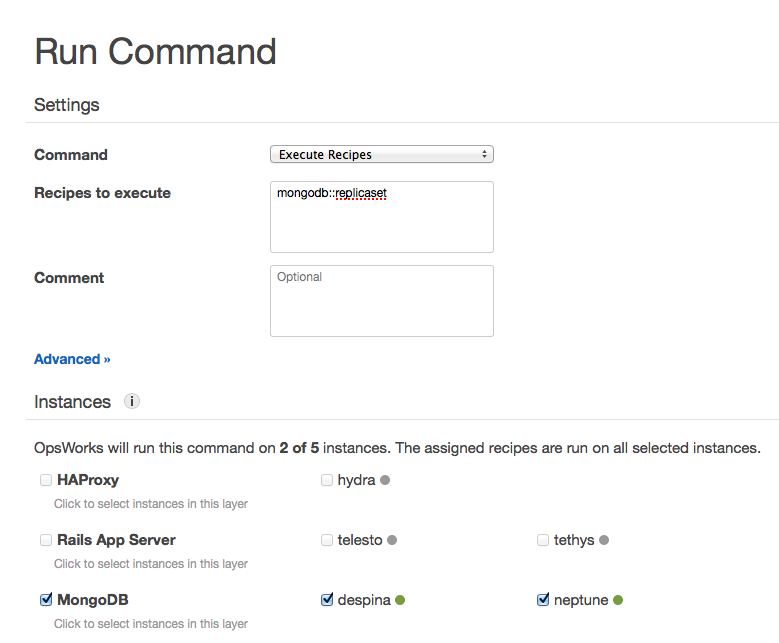
*Note: MongoDB instance names changed because I removed the nodes before realizing the original screenshot did not get saved properly.
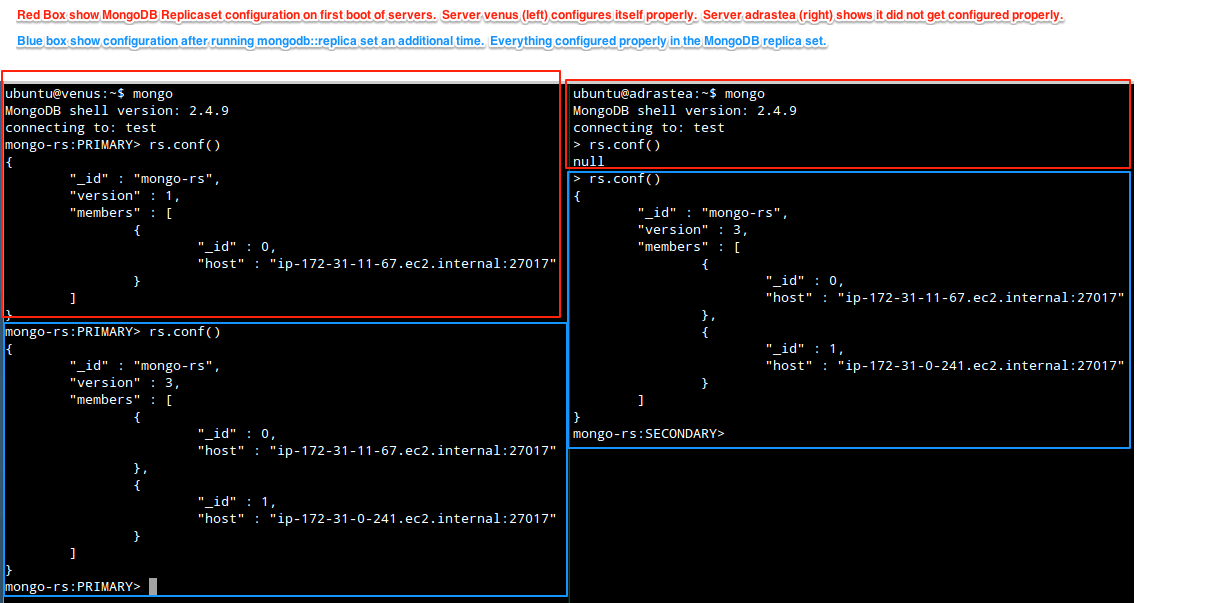
Verifying the configuration
If everything was successful, you should be able to ssh to your MongoDB
instances and look at the MongoDB configuration with the commands
mongo to connect to the instance and rs.conf() to show the
current replicaset configuration.
This screenshot shows the before and after of the above mentioned
mongodb::replicaset command work-around.